O-RAN O-DU Testing

This guide describes how to test an O-DU using Paragon-neo to ensure its behaviour meets the requirements specified in the CONF document for devices to be deployed in an LLS-C1, LLS-C2, LLS-C3 or LLC-C4 topology.
O-RAN O-RU Testing

This guide describes how to test an O-RU using Calnex's Paragon-neo to ensure that its behavior meets the requirements specified in the CONF document for devices being deployed in an LLS-C1 or LLS-C2 topology.
O-RAN: Proving Time Accuracy for the Fronthaul Network

This document provides an overview of O-RAN, descriptions of its technical specifications for the Synchronization Plane (S-Plane), and test recommendations to support a robust and efficient fronthaul network.
Testing a PRTC to ITU-T G.8272

This Test Guide shows how the Calnex Paragon-neo can be used to test that a Primary Reference Time Clock (PRTC) complies to the timing requirements given in the ITU-T G.8272 standard.
OPEN Alliance: TC11 Time Sync Testing

This Test Guide shows how the Calnex Paragon-X can be used to prove IEEE 802.1AS (gPTP) supporting devices are compliant to OPEN Alliance TC11 2.5 Test Specifications, and provides procedures to measure timing accuracy.
G.8273.2 BC Conformance Test

This Test Guide shows how the Calnex Paragon-neo can be used to test T-BC compliance as per G.8273.2 and provides procedures to measure noise generation, time noise tolerance and transfer, packet layer transient response and holdover performance.
G.8273.2 T-TSC Conformance Test

This Test Guide shows how the Calnex Paragon-neo can be used to test T-TSC compliance as per G.8273.2 and provides procedures to measure noise generation, time noise tolerance and transfer, packet layer transient response and holdover performance.
G.8273.4 Conformance Test

This Test Guide shows how the Calnex Paragon-neo can be used to test T-BC and T-TSC compliance as per G.8273.4 and provides procedures to measure noise generation, tolerance and transfer, transient response, and holdover performance.
G.8262.1/G.8262 EECs Conformance Test

This Test Guide shows how the Paragon-neo can be used to perform the tests specified in the ITU-T G.8262.1/G.8262 standards for proving SyncE wander and jitter performance at rates up to 100GbE. The tests include noise generation, noise tolerance and transfer, phase transient response and holdover performance.
Time Aware End Station: Time Error Testing

This Test Guide shows how the Calnex Paragon-X can be used to prove Time Aware End Station compliance to IEEE 802.1AS (gPTP) and provides procedures to measure noise generation and time noise tolerance.
Testing a T-BC to ITU-T G.8273.2

The accuracy of Telecom Boundary Clocks (T-BCs) is essential to the successful roll-out of 5G, in addition to supporting LTE-A and TDD-LTE. The ITU-T has updated specifications for T-BCs in Recommendation G.8273.2 to cover this range of applications. This Technical Overview describes what a boundary clock is, and explains the critical performance parameters defined in G.8273.2.
G.8262 SyncE Conformance Testing
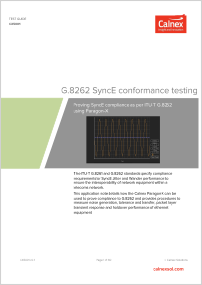
The ITU-T G.8261 and G.8262 standards specify compliance requrements for SyncE Jitter and Wander performance. This application note detail how the Calnex Paragon-X can be used to prove compliance to G.8262 and provides procedures to measure noise generation, tolerance and transfer, packet layer transient response and holdover performance of Ethernet equipment.
Stepping Up to the Challenge

With mobile communications, some of the current and proposed future radio technologies require not only frequency sync, but time sync as well. In this paper Tommy Cook and Tim Frost will discuss the challenge of tighter time accuracy.
Testing Performance of a Smart SFP Transparent Clock

The Chronos Smart SFP™ can be configured as a T-TC, allowing Network Operators to use existing network equipment. This Application note describes how the T-TC performance can be verified by the Calnex Paragon-X.
Managing the Impact of Cable Delays

A discussion on the issues that need to be considered and some tips on how to ensure the uncertainty due to cable delays is minimised when performing high accuracy Time Error measurements.
Technical Brief for Boundary Clocks
The accuarcy of Telecom Boundary Clocks is essential to the successful roll-out of LTE-A and TDD-LTE. The ITU-T has agreed a new specification for the performance of T-BCs, recommendation G.8273.2. This application note describes what a Boundary Clock is, and explains the critical performance parameters defined in G.8273.2.
Time Error Results

Issues that need to be considered for accurate Time Error results including comment on 1pps measurements, 1588 Time Error measurement, telecom boundary clock (T-BC), Polarity of T-BC inaccuracies and a summary of T-BC inaccuracies.
T-TSC Time Error

The accuracy of Telecom Time Slave Clocks (T-TSCs) is essential to the successful roll-out of LTE-A and TDD-LTE. To meet the new G.8273.2 compliance limits, T-TSCs must meet a very stringent constant Time-Error (cTE) limit of 20 or 50 nanoseconds.
T-BC Time Error

This Test Guide shows how the Calnex Paragon-X can be used to prove T-BC compliance to G.8273.2 and provides procedures to measure noise generation time noise tolerance and transfer, packet layer transient response and holdover performance.
Time Error Transfer of G.8273.2 T-BCs

The companion Technical Overview, "Testing a T-BC to ITU-T G.8273.2" describes the methods of testing a telecom boundary clock (T-BC) to meet G.8273.2. This Technical Overview describes in more detail the methods for measuring time error transfer of a T-BC, following the recommendations of G.8273.2 Appendix VI.
Time Aware Relay: Time Error Testing

This Test Guide shows how the Calnex Paragon-X can be used to provide Time Aware Relay compliance to IEEE 802.1AS (gPTP) and provides procedures to measure noise generation and time noise tolerance.
Time Transfer in Industrial Ethernet Applications

This document provides an overview of the benefits and challenges when choosing a PTP Profile for a particular application, discusses appropriate hardware and software capabilities for network equipment, and examines the impact of different network environments on time accuracy.
Proving Time Accuracy for Automotive Systems

This document outlines how IEEE 802.1AS (gPTP) provides the high-accuracy synchronization which is the foundation of Time Sensitive Networking (TSN), what the challenges are for testing and developing Automotive gPTP, and recommended best practice for proving synchronization performance of devices and networks.
Professional Broadcast Networks

As IP networks become more prevalent in professional broadcast environments, accurate synchronization using the Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is becoming a critical consideration. This paper provides background on PTP, and details on the SMPTE ‘Broadcast’ Profile.
Testing Synchronization for Industrial TSN

This document outlines how IEEE 802.1AS (gPTP) provides the high-accuracy synchronization which is the foundation of Time Sensitive Networking (TSN), what the challenges are for testing and developing gPTP, and recommended best practice for proving synchronization performance of devices and networks.
MiFID Time Compliance

This document gives an overview of the requirements for time accuracy and traceability to MiFID II, background information on Precision Time Protocol (PTP) and the part it plays in satisfying these requirements, and considerations for proving equipment is fit for purpose as well as demonstrating that networks are compliant to MiFID II as per RTS 25 - levels of accuracy for business clocks.
PTP Profile Compliance

The Precision Time Protocol (PTP) allows precise timing over Ethernet, but interoperability challenges can be a major barrier to deployment. This document explains the benefits - and challenges - of mutiple PTP profiles, and possible test solutions.
Time and Time Error

This Technical Overview discusses how time is distributed over the network, how Time Error affects network performance, and methods to mitigate Time Error to ensure accurate timing and synchronization throughout the network.
